Nếu bạn cài Oracle Grid Infrastructure 21c trên môi trường đồ họa thì ở mỗi bước cài sẽ có nút Help để bạn đọc coi phần này nói về cái gì.
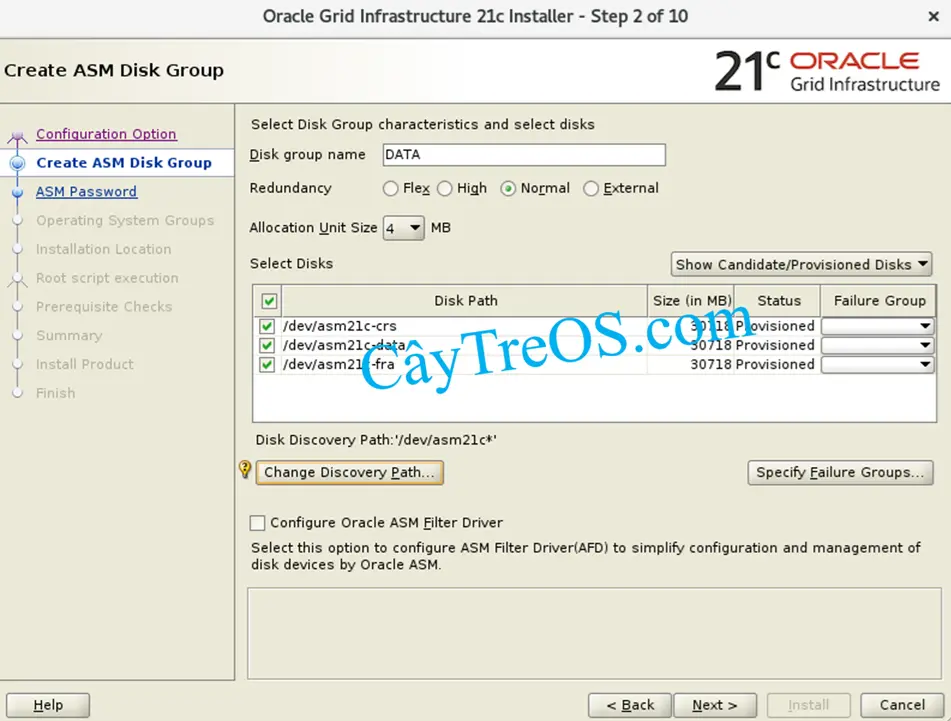
Nếu bạn thắc mắc về tạo Oracle ASM Disk Group có những kiểu gì và mỗi kiểu có mục đích gì thì hãy đọc hướng dẫn của Oracle ở phần dưới.
Create ASM Disk Group
Provide the name of the initial disk group you want to configure in the Disk Group Name field.
The Add Disks table displays disks that are configured as candidate disks. Select the number of candidate or provisioned disks (or partitions on a file system) required for the level of redundancy that you want for your first disk group.
For standard disk groups, High redundancy requires a minimum of three disks. Normal requires a minimum of two disks. External requires a minimum of one disk. Flex redundancy requires a minimum of three disks.
Oracle Cluster Registry and voting files for Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a cluster are configured on Oracle ASM. Hence, the minimum number of disks required for the disk group is higher. High redundancy requires a minimum of five disks. Normal redundancy requires a minimum of three disks. External redundancy requires a minimum of one disk. Flex redundancy requires a minimum of three disks.
If you are configuring an Oracle Extended Cluster installation, then you can also choose an additional Extended redundancy option. The number of supported sites for extended redundancy is three. For extended redundancy with three sites, for example, two data sites, and one quorum failure group, the minimum number of disks is seven. For an Oracle Extended Cluster, you also need to select the site for each failure group.
Voting disk files require a higher number of minimum disks to provide the required separate physical devices for quorum failure groups, so that a quorum of voting disk files are available even if one failure group becomes unavailable. You must place voting disk files on Oracle ASM, therefore, ensure that you have enough disks available for the redundancy level you require.
If you selected redundancy as Flex, Normal, or High, then you can click Specify Failure Groups and provide details of the failure groups to use for Oracle ASM disks. Select the quorum failure group for voting files.
If you do not see candidate disks displayed, then click Change Discovery Path, and enter a path where Oracle Universal Installer (OUI) can find candidate disks. Ensure that you specify the Oracle ASM discovery path for Oracle ASM disks.
Select Configure Oracle ASM Filter Driver to use Oracle Automatic Storage Management Filter Driver (Oracle ASMFD) for configuring and managing your Oracle ASM disk devices. Oracle ASMFD simplifies the configuration and management of disk devices by eliminating the need to rebind disk devices used with Oracle ASM each time the system is restarted.
See Oracle Automatic Storage Management Administrator's Guide for more information about configuring Oracle ASM Filter Driver.
For additional information, review the following sections:
What is an Oracle ASM Disk Group
An Oracle ASM disk group consists of multiple disks. The disk group is the fundamental object that Oracle ASM manages. Each disk group contains the metadata that is required for the management of space in the disk group. Files are allocated from disk groups. Any Oracle ASM file is completely contained within a single disk group. However, a disk group might contain files belonging to several databases and a single database can use files from multiple disk groups. For most installations you need only a small number of disk groups, usually two, and rarely more than three. Disk group components include disks, files, and allocation units.
What is a Candidate Disk
A Candidate Disk is a disk that is not part of an existing disk group. If you want to use a disk that was used previously in an ASM disk group, and was not deleted properly from the disk group (as in an incomplete installation), then delete existing information on the disk so that it can be recognized as a candidate disk.
Redundancy Options
Redundancy, or mirroring, is the process of replicating the contents of a file in another location. Redundancy protects data integrity by storing copies of data on multiple disks. The disk group type determines the mirroring levels with which Oracle creates files in a disk group.
When you create a disk group, you specify an Oracle ASM disk group type based on one of the following redundancy levels:
High: Uses three-way mirroring of Oracle ASM metadata and user data. A high redundancy disk group requires a minimum of three disk devices (or three failure groups). The effective disk space in a high redundancy disk group is one-third the sum of the disk space in all of its devices. A high redundancy disk group can tolerate two failures.
Flex: Uses three-way mirroring of Oracle ASM metadata. You can decide the mirroring for user data, from unprotected, or mirrored, or high. A flex redundancy disk group is a type of redundancy disk group with features such as flexible file redundancy, mirror splitting, and redundancy change. A flex disk group can consolidate files with different redundancy requirements into a single disk group. It also provides the capability for a database to change the redundancy of its files. A flex redundancy disk group requires a minimum of three disk devices (or three failure groups). Flex redundancy disk groups with five or more failure groups can tolerate two failures. Flex disk groups with three or four failure groups can tolerate only one failure.
Normal: Uses two-way mirroring. A normal redundancy disk group requires a minimum of two disk devices (or two failure groups).
External: Choosing not to use ASM mirroring of files, commonly when you provide mirroring using another technology, such as a Redundant Array of Independent (or Inexpensive) Disks (RAID).
Extended: If you are configuring an Oracle Extended Cluster installation, then you can also choose an additional Extended redundancy option. Extended redundancy uses two or three-way mirroring for each site, as specified in the file group attribute. Extended redundancy disk group has similar features as the flex redundancy disk group. Extended redundancy extends Oracle ASM data protection to cover failure of sites by placing enough copies of data in different failure groups of each site. For extended redundancy with three sites, for example, two data sites, and one quorum failure group, the minimum number of disks is seven.
The disk group type determines the mirroring levels with which Oracle creates files in a disk group. The redundancy level controls how many disk failures are tolerated without dismounting the disk group or losing data.
Allocation Unit Size (AU Size)
Every Oracle ASM disk is divided into allocation units (AU). An allocation unit is the fundamental unit of allocation within a disk group. A file extent consists of one or more allocation units. An Oracle ASM file consists of one or more file extents.
When you create a disk group, you can set the Oracle ASM allocation unit size with the AU_SIZE disk group attribute. The values can be 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, or 64 MB, depending on the specific disk group compatibility level. Larger AU sizes typically provide performance advantages for data warehouse applications that use large sequential reads.
The default value is set to 4 MB.
Oracle ASM Filter Driver
The Oracle ASM Filter Driver (Oracle ASMFD) is installed by default with Oracle Grid Infrastructure. Oracle ASMFD rejects write I/O requests that are not issued by Oracle software. This filter ensures that users with administrative privileges cannot inadvertently overwrite Oracle ASM disks, thus preventing corruption in Oracle ASM disks and files within the disk group. For disk partitions, the area protected is the area on the disk managed by Oracle ASMFD, assuming the partition table is left untouched by the user.
Oracle ASMFD simplifies the configuration and management of disk devices by eliminating the need to rebind disk devices used with Oracle ASM each time the system is restarted.


